A University of Kansas survey of a swath of the cosmos using the James Webb Space Telescope has revealed active galactic nuclei (AGN)—supermassive black holes that are rapidly increasing in size—are rarer than many astronomers had assumed previously.
The findings, made with the JWST’s Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI), suggest our universe may be a bit more stable than was supposed. The work also gives insights into observations of faint galaxies, their properties and challenges in identifying AGN.
A new paper detailing the JWST research, conducted under auspices of the Cosmic Evolution Early Release Science (CEERS) program, was made available on arXiv in advance of formal peer review publication in The Astrophysical Journal.
The work, headed by Allison Kirkpatrick, assistant professor of physics & astronomy at KU, focused on a long-studied zone of cosmos dubbed the Extended Groth Strip, located between the Ursa Major and Boötes constellations. But previous examinations of the area relied on a less powerful generation of space telescopes.
“Our observations were taken in last June and December, and we were aiming to characterize how galaxies looked during the heyday of star formation in the universe,” Kirkpatrick said. “This is a look back in time of 7 to 10 billion years in the past. We used the mid-infrared instrument on the James Webb Space Telescope to look at dust in galaxies that are existing 10 billion years in the past, and that dust can hide ongoing star formation, and it can hide growing supermassive black holes. So I carried out the first survey to search for these lurking, supermassive black holes at the centers of these galaxies.”
While every galaxy features a supermassive black hole at the middle, AGN are more spectacular upheavals actively drawing in gases and showing a luminosity absent from typical black holes.
Kirkpatrick and many fellow astrophysicists anticipated that the higher-resolution JWST survey would locate many more AGN than a previous survey, conducted with the Spitzer Space Telescope. However, even with MIRI’s boost in power and sensitivity, few additional AGN were found in the new survey.
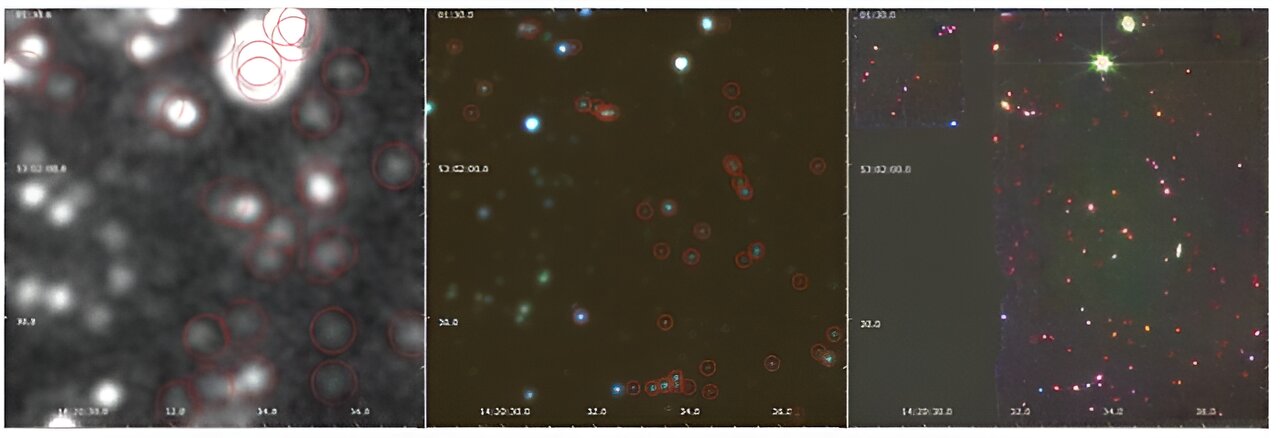
“The results looked completely different from what I had anticipated, leading to my first major surprise,” Kirkpatrick said. “One significant revelation was the scarcity of rapidly growing supermassive black holes. This finding was prompting questions about the whereabouts of these objects. As it turns out, these black holes are likely growing at a slower pace than previously believed, which is intriguing, considering the galaxies I examined resemble our Milky Way from the past. Earlier observations using Spitzer only allowed us to study the brightest and most massive galaxies with rapidly growing supermassive black holes, making them easy to detect.”
Kirkpatrick said an important mystery in astronomy lies in understanding how typical supermassive black holes, such as those found in galaxies like the Milky Way, grow and influence their host galaxy.
“The study’s findings suggest that these black holes are not growing rapidly, absorbing limited material, and perhaps not significantly impacting their host galaxies,” she said. “This discovery opens up a whole new perspective on black-hole growth since our current understanding is largely based on the most massive black holes in the biggest galaxies, which have significant effects on their hosts, but the smaller black holes in these galaxies likely do not.”
Another surprising outcome was the lack of dust in these galaxies, said the KU astronomer.
“By using JWST, we can identify much smaller galaxies than ever before, including those the size of the Milky Way or even smaller, which was previously impossible at these redshifts (cosmic distances),” Kirkpatrick said. “Typically, the most massive galaxies have abundant dust due to their rapid star formation rates. I had assumed that lower mass galaxies would also contain substantial amounts of dust, but they did not, defying my expectations and offering another intriguing discovery.”
According to Kirkpatrick, the work changes understanding of how galaxies grow, particularly concerning the Milky Way.
“Our black hole seems quite uneventful, not displaying much activity,” she said. “One significant question regarding the Milky Way is whether it was ever active or went through an AGN phase. If most galaxies, like ours, lack detectable AGN, it could imply that our black hole was never more active in the past. Ultimately, this knowledge will help constrain and measure black hole masses, shedding light on the origins of black holes growing, which remain an unanswered question.”
Kirkpatrick recently earned significant new time on JWST to carry out a larger survey of the Extended Groth Strip field with MIRI. Her current paper included about 400 galaxies. Her upcoming survey (MEGA: MIRI EGS Galaxy and AGN survey) will include about 5,000 galaxies. The work is planned for January 2024.
Reference:
Allison Kirkpatrick et al, CEERS Key Paper VII: JWST/MIRI Reveals a Faint Population of Galaxies at Cosmic Noon Unseen by Spitzer, arXiv (2023). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2308.09750
Perhaps smaller blackholes simply ran out of dust to hoover up… which suggests black holes have a limit on the size of what they can attract and absorb… possibly helping to explain the absence of the expected plentiful AGNs.
nc
A thought: Matter may be produced in stars from dark matter to produce its own fuel hydrogen. Dark matter being the particle and dark energy being the spin c of that particle moving electrons and light. Matter as we recognize it has entropy while the propagation of light and other spectrum waves do not. The largest stars grow to a point where their gravity becomes equal to the speed of light and the energy moving the electrons can no longer keep the protons from fusing into a neutron star or a blackhole. This leaving the dust particles to create new stars. Energy c could be slowing down and we could not detect a slow down. Our universe could be a super galaxy spinning causing part of the red shift along with the dilation of light produced in GR center of galaxies. After all something has to be the cause of dilation and equivalence between SR and GR. Dilation of c particles would increase the distance between those particles reducing energy density so your meter stick expands by the same distance light travels to measure time the same in every frame.
Look at the three clocks that measure time equally in synchronization between frames. Mechanical, atomic and light clocks.
The dual slit experiment when you watch electronically polarizes the spectrum energy causing the two slits vs. the flexibility when it’s not polarized. Particles in a 3d universe can not be equal distanced from each other but polarization can freeze them in place.
Quantum mechanics cause Relativity.